In this article, we will introduce you to the concept of block halving. To do this, you first need to know some additional information.
How are new coins mined by miners?
What is mining, or in English, “digging” cryptocurrencies? Being a “miner” on the blockchain network involves solving complex mathematical puzzles. In order to be able to make difficult calculations, we need hardware with high computing power. Once the puzzle is solved, a new block is created on the blockchain network. In the case of Bitcoin (BTC), a new block is created on average every 10 minutes, joining the global P2P network. For “digging” a new block, i.e. a new node, each “miner” receives a so-called block reward, i.e. a certain amount of coins.
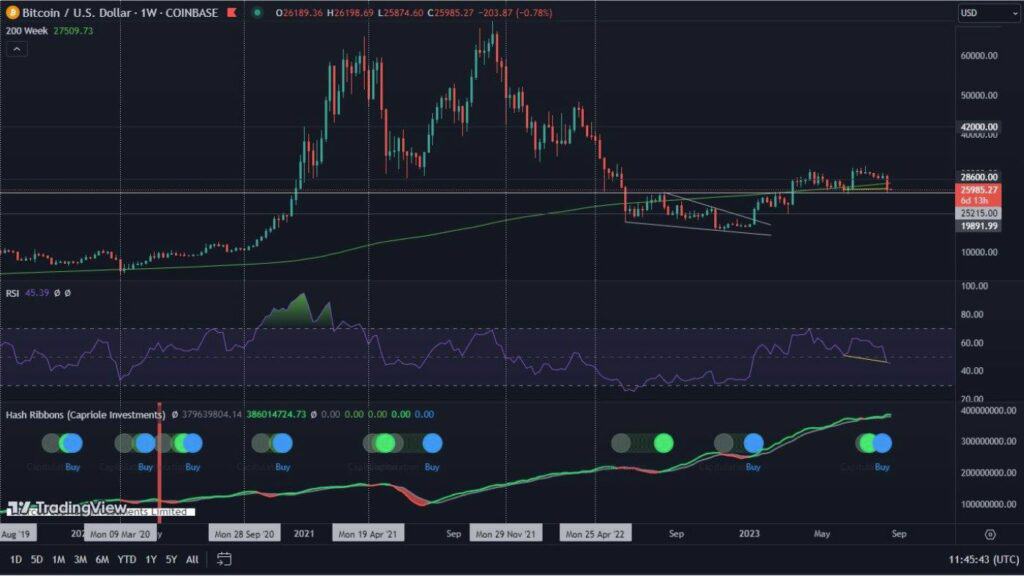
Deflation on the example of Bitcoin (BTC)
If you are rewarded with coins for “digging” cryptocurrencies, is this an infinite source of profit? If you are new to the world of cryptocurrencies, this is probably the question that has popped into your head. Unfortunately, the answer is no. We’ll use one of the most popular cryptocurrencies, Bitcoin (BTC), as an example. Bitcoin is a deflationary currency, which means that its supply is predetermined. Therefore, more coins cannot be mined because the number of coins is predetermined. Currently, new coins are being mined by “miners” all the time, while the bonus, or reward (amount of new coins) that a “miner” receives for mining a new block is decreasing all the time. The implication is that Bitcoin inflation is heading towards zero. It is projected to reach this level in 2040.
What is block halving?
In this case, we seamlessly move to a new term: blockhalving. Blockhalving is called an action that aims to reduce the influx of new coins of a specific cryptocurrency. As we mentioned in the previous paragraph, the reward for mining a new node is periodically reduced. We will again use Bitcoin (BTC) as an example cryptocurrency to better understand the concept of blockhalving.
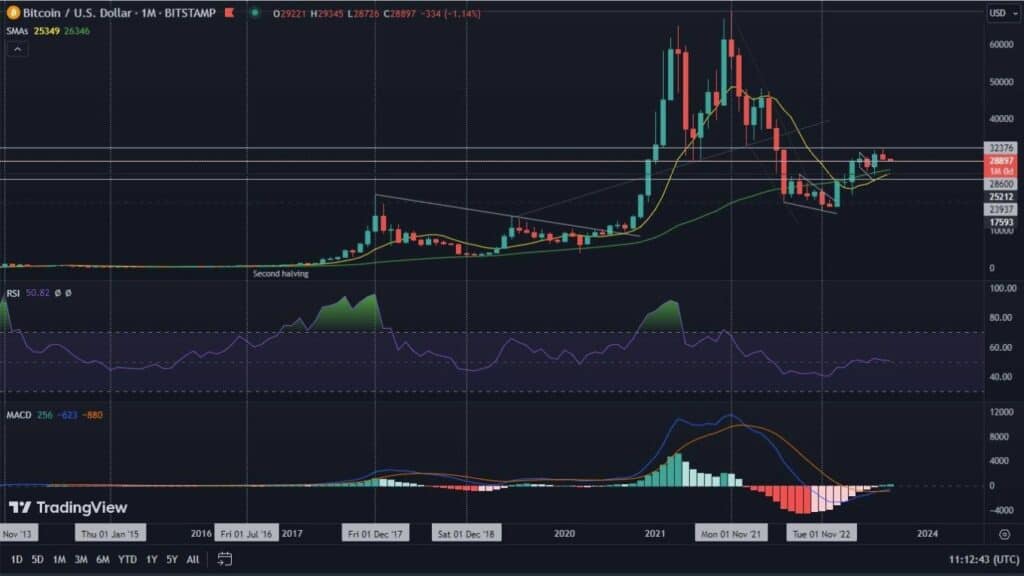
After every 210,000 blocks mined, which is roughly every four years, the block reward, which is the reward given to Bitcoin “miners” for mining a new block, is halved. By doing this, it also halves the rate at which new Bitcoin is put into circulation. In this way, Bitcoin uses an artificial form of inflation, which is halved every four years until all Bitcoins have been “mined.”
So far in Bitcoin’s history, three blockhalvings have occurred. The first one was in 2009, when the reward for each mined block in the chain was 50 Bitcoins, while after the first halving it was 25. The next one occurred in 2016. Then the reward was 12.5 Bitcoin. Whereas from May 11, 2020, the reward is 6.25 bitcoin per block.